Table of Contents
Scrum is the agile methodology or process in which a set of best practices are applied to facilitate collaborative work between teams and thus obtain the best results in the project development of projects. This agility allows the product or service to be launched to the market quickly and start obtaining sales and profits.
The scrum methodology is a framework mostly used by development teams, although its philosophy and best practices can be applied to any other department that requires teamwork.
The goal of scrum is to maximize the company’s return on investment (ROI).
Scrum: effective project management
In the scrum methodology, work is based on Sprint where each part of the project is planned in advance and once that part is finished, the work that has been previously validated is reviewed. Thanks to this analysis the team can detect what is not working correctly, what resources are needed and with this data, the following sprints can be planned effectively.
Scrum reveals visible the relative effectiveness of the current management, environment and work rules so that improvements can be made. The Scrum methodology is able to detect when a customer does not receive what was agreed, when the deliveries of each Sprint are extended in time, if the costs are skyrocketing, and all kinds of inefficiencies that slow down the delivery and quality of the product.
With Scrum it is possible to control and remedy possible deviations that occur during the development of a project.

Scrum values
There are 3 elements that cannot be left aside when working with Scrum methodology:
Transparency
The process and the work must be visible to both the team developing the project and to those who will receive it.
This ensures that there is a common understanding and a global vision.
Inspection
Project progress should be inspected frequently and diligently to detect potentially undesirable problems.
Inspection allows for adaptation.
Adaptation
When a change arises in the development of the project, the team must adapt to achieve the objective of the Sprint.
Thanks to this adaptation, the success of complex projects is achieved, since it is in these projects where the most changing requirements occur.
Teamwork based Scrum
Scrum is based on the collective intelligence of the people who use it: instead of providing people with detailed instructions, Scrum best practices guide their relationships and interactions, thus achieving collaborative teamwork to achieve the best possible project outcome.
This methodology recognizes and takes into account that the team does not know everything at the beginning of the project and that the project will evolve through experience. Scrum is designed to help teams adapt naturally to changing conditions and new customer requirements.
It takes into account aspects such as:
- Adaptation to changes and new requirements during the development of a project
- Customer collaboration
- Continuous development adapting to new requirements and solving possible inconveniences that may arise during the continuity of the project.
The Scrum Team
Scrum Teams are cross-functional: each one is responsible for their tasks and for meeting their deadlines, thus, the project develops successfully without the supervision of other members of the organization.
Scrum defines 3 very significant roles within its methodology.

Product Owner
He is the product owner and is responsible for maximizing the value of the product developed by the development team and is, at the same time, the customer’s representative within this multi-disciplinary team.
The Product Owner is ultimately responsible for managing the Product Backlog.
Each Scrum Team has only one Product Owner, who can also be part of the development team.
Learn more about the Product Owner in our article: “What is and what are the functions of the Product Owner“.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is in charge of supervising that Scrum techniques are understood and applied in the company. Not to be confused with the Product Owner, who has a more business perspective, while the Scrum Master is in charge of ensuring that the entire team understands what Scrum is and applies it correctly.
Learn more about the Scrum Master in our article: “What is Scrum Master“.
Development Team
The Development Team is a self-organized cross-functional team and is in charge of defining the tasks.
It is composed of professionals who perform the work of delivering a “Done” product Increment. Only members of the Development Team participate in the creation of the Increment.
Without them, it matters little to have the best Product Owner or Scrum Master, since it is the team that will ultimately develop the product.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are the group of people who influence the company, such as employees, suppliers, or shareholders.
Stakeholders are the group of people affected by the decisions made in a company. They could not be considered as a proper role within the Scrum methodology, but they do offer continuous feedback on the company’s products, which is why they are allowed to participate in the Sprint Review.
One of the functions of the Product Owner is to channel the wishes and needs of the Stakeholders through the Product Backlog.
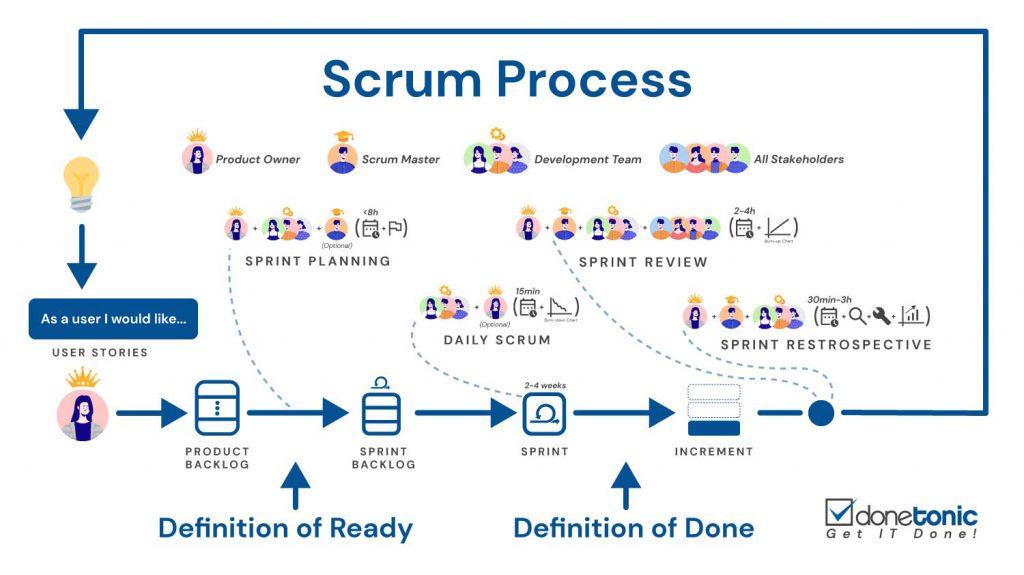
Scrum Events
The development of a product is carried out within a Sprint that contains the following phases:

Sprint
Sprints are the foundation of Scrum, it is where ideas are converted into value and are initiated immediately when the conclusions of the previous Sprint are obtained.
They are usually events that last about two weeks, sometimes up to four, so that the project does not lose coherence or dissipate over time, as long Sprints can cause feedback with the customer to be lost.
Sprint Planning
It is the meeting in which the Scrum Team defines what tasks are to be performed and what will be the objective of the Sprint and will be defined by all members of the Scrum Team.
In this first meeting, the Product Owner ensures that all members are able to define the most important elements of the Product Backlog.
The following questions should be addressed:
- What does this Sprint deliver? The Product Owner proposes how the product can increase its value and its objective must be defined before the end of the Sprint planning. Based on this objective, some tasks or others will be defined.
- How will it be addressed? The development team will define the tasks added in a product list that will be needed to complete the Sprint objective.
- How will it be done? For each task on that product list the development team will plan the work required.
Daily Scrum Meeting
The Daily Scrum Meeting is held daily, it is a meeting of about 15 minutes in which the Development Team and the Scrum Master participate and it is recommended that it is always held at the same time and in the same place to reduce complexity.
These meetings are intended to improve communications, to identify drawbacks and impediments, and to promote quick decisions. They are used to achieve the adaptation of tasks in case of changes within the Sprint.
Sprint Review
The Sprint Review is performed at the end of each Sprint and serves to show the customer the result of the work developed in the Sprint.
The Product Owner, the customer and the development team are all in attendance. The Product Owner presents the development to the customer and the development team, its operation. And it is in this Sprint Review where the customer provides feedback and asks the Product Owner for new tasks to be added to the Product backlog.
Sprint Retrospective
It is the last element of the Sprint and it is the meeting where conclusions are drawn on how the Scrum methodology has been implemented in the last Sprint.
It should serve to propose improvements to the Scrum team itself in the face of the new Sprint and thus improve in each one of them, becoming a much more effective team and providing greater value to the final product.
In the following article we explain the difference between Sprint Review and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum Artifacts
Scrum artifacts are intended to maximize information transparency so that all Scrum team members have the same understanding of the artifact.
Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is an ordered list of everything needed in the product and is the sole source of requirements for any changes to be made to the product.
This Backlog is never complete, it is dynamic and evolves as the product and its environment always do to identify what the product needs to be adequate, competitive and useful. As long as the product exists, the Product Backlog will always exist.
The attributes of the Product Backlog are: description, order, estimate and value.
Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog is the set of Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint.
It makes visible all the work that the Development Team identifies as necessary to achieve the Sprint Goal.
When new work is required, the Development Team adds it to the Sprint Backlog and as the work is executed the remaining work estimate is updated.
Increment
Finally, the Increment is the sum of all the elements of the Product Backlog that have been completed during a Sprint plus the value of the increments of all the previous Sprints.
When a Sprint ends the new Increment must be “Finished” according to the Scrum Team Definition of “Finished”.
You can learn more about Scrum at ScrumAlliance.org.